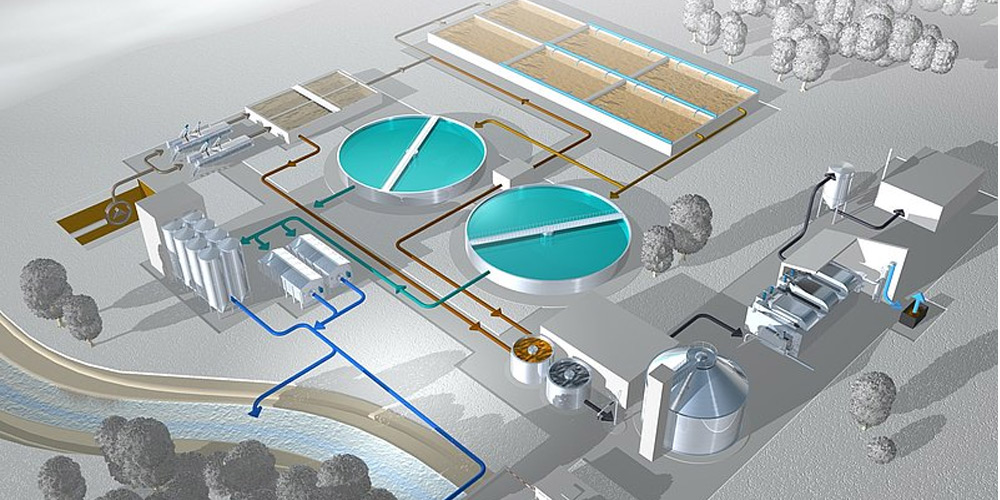
Агын сууларды тазалоо процессинде полиакриламид (PAM) маанилүүфлокулянт, суунун сапатын жакшыртуу үчүн кеңири колдонулат. Бирок, көп учурда PAMдын ашыкча дозасы пайда болот, бул агынды сууларды тазалоонун натыйжалуулугуна гана таасир этпестен, айлана-чөйрөгө терс таасирин тийгизиши мүмкүн. Бул макалада PAMдын ашыкча дозасы менен байланышкан көйгөйлөрдү кантип аныктоо, алардын себептерин талдоо жана тиешелүү чечимдерди сунуштоо каралат.
Ашыкча ПАМ дозасынын белгилери
Ашыкча PAM кошулганда, төмөнкү көйгөйлөр пайда болушу мүмкүн:
Начар флокуляция эффектиси: PAM дозасы көбөйгөнүнө карабастан, суу булуттуу бойдон калууда жана флокуляция эффектиси жетишсиз.
Анормалдуу чөкмө: Бактагы чөкмө майдаланып, бошоп, чөгүшү кыйын болуп калат.
Чыпканын бүтөлүп калышы: АшыкчаPAM флокулянтысуунун илешкектүүлүгүн жогорулатат, бул чыпканын жана түтүктөрдүн бүтөлүп калышына алып келет, ошондуктан тез-тез тазалоону талап кылат.
Агынды суулардын сапатынын начарлашы: Агынды суулардын сапаты бир кыйла төмөндөйт, булгоочу заттардын деңгээли стандарттардан ашып түшөт. Ашыкча PAM суунун молекулярдык түзүлүшүнө таасир этет, COD жана BOD курамын жогорулатат, органикалык заттардын ажыроо ылдамдыгын төмөндөтөт жана суунун сапатын начарлатат. PAM ошондой эле суу микроорганизмдерине таасир этип, жыт көйгөйлөрүн жаратышы мүмкүн.
ПАМдын ашыкча дозасынын себептери
Тажрыйбанын жана түшүнүүнүн жетишсиздиги: Операторлор PAM дозалоо боюнча илимий билимге ээ эмес жана чектелүү тажрыйбага гана таянышат.
Жабдуулардын көйгөйлөрү: Өлчөөчү насостун же агым өлчөгүчтүн иштебей калышы же катасы дозанын туура эмес көрсөтүлүшүнө алып келет.
Суунун сапатынын өзгөрүшү: Суунун сапатынын олуттуу өзгөрүүлөрү ПАМдын дозасын көзөмөлдөөнү кыйындатат.
Операциялык каталар: Оператордун каталары же жазуудагы каталар ашыкча дозага алып келет.
Чечимдер
PAM ашыкча дозасын азайтуу үчүн төмөнкү чараларды көрүү керек:
Окутууларды күчөтүү: Операторлорго PAM дозасын түшүнүү жана иштөө жөндөмүн жогорулатуу үчүн кесиптик окутууларды өткөрүү. PAMдын туура дозасы оптималдуу флокуляциялык эффекттерди камсыз кылат.
Жабдууларды техникалык тейлөөнү оптималдаштыруу: Тактыгын жана ишенимдүүлүгүн камсыз кылуу үчүн өлчөөчү насосторду, агым өлчөгүчтөрдү жана башка жабдууларды үзгүлтүксүз текшерип жана техникалык тейлөөдөн өткөрүп туруңуз.
Суунун сапатын көзөмөлдөөнү күчөтүү: Суунун сапатынын өзгөрүшүн тез аныктоо үчүн суунун сапатын көзөмөлдөө жыштыгын көбөйтүү.
Иштөө мүнөздөмөлөрүн түзүү: PAM кошуу кадамдарын жана сактык чараларын баяндаган деталдуу иштөө жол-жоболорун иштеп чыгуу.
Акылдуу башкарууну киргизүү: Адамдык катаны минималдаштыруу үчүн автоматтык түрдө PAM дозасын эсептөө үчүн акылдуу башкаруу системасын ишке ашыруу.
Дозасын өз убагында тууралаңыз: Суунун сапатын көзөмөлдөөгө жана иш жүзүндөгү операцияларга таянып, флокуляциянын туруктуу таасирин жана агынды суунун сапатын сактоо үчүн PAM дозасын өз убагында тууралаңыз.
Байланышты жана кызматташтыкты күчөтүү: Маалыматтын үзгүлтүксүз агымын камсыз кылуу жана PAMдын ашыкча дозаланышы маселелерин биргелешип чечүү үчүн бөлүмдөрдүн ортосундагы байланышты жана кызматташууну өнүктүрүү.
Кыскача баяндама жана сунуштар
Ашыкча PAM дозасын алдын алуу үчүн, агынды сууларды тазалоодо PAM кошулушун кылдаттык менен көзөмөлдөө маанилүү. Дозаны ар кандай көз караштардан байкоо жана талдоо керек, ал эми адистер көйгөйлөрдү тез арада аныктап, чечиши керек. Ашыкча PAM дозасын азайтуу үчүн окутууну күчөтүүнү, операцияларды стандартташтырууну, жабдууларды тейлөөнү оптималдаштырууну, суунун сапатын көзөмөлдөөнү күчөтүүнү жана акылдуу башкаруу системаларын киргизүүнү карап көрүңүз. Бул чаралар аркылуу PAM дозасын натыйжалуу көзөмөлдөөгө, агынды сууларды тазалоонун натыйжалуулугун жогорулатууга жана айлана-чөйрөнүн сапатын коргоого болот.
Жарыяланган убактысы: 2024-жылдын 25-октябры